Wound Care For Diabetic Feet: Best Practices And Techniques
Wound care for diabetic feet is a critical aspect of managing diabetes-related complications and preventing serious health issues such as infections and amputations. Diabetic individuals are at a higher risk of developing foot ulcers due to neuropathy and poor circulation, making proper wound care essential for maintaining foot health. In this article, we will explore the best practices and techniques for wound care in diabetic feet, focusing on prevention, treatment, and management strategies.
Importance of Wound Care for Diabetic Feet
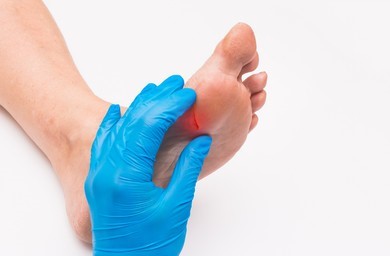
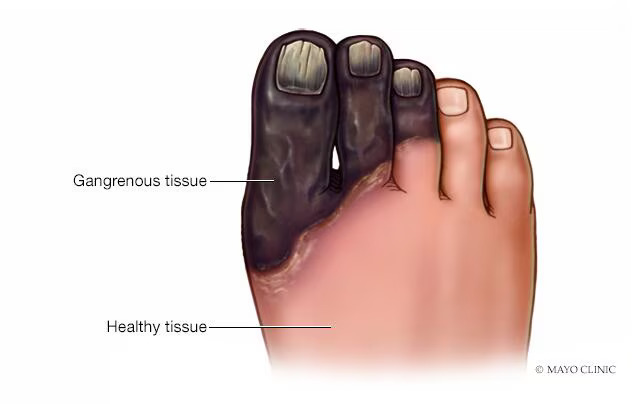
Diabetic foot ulcers are a common and serious complication of diabetes, with approximately 15% of diabetic individuals experiencing foot ulcers in their lifetime. These ulcers can lead to infections, tissue damage, and even amputations if not properly treated and managed. Proper wound care is essential for preventing complications, promoting healing, and preserving foot function and mobility in diabetic individuals.
Best Practices for Wound Care
- Daily Inspection: Diabetic individuals should inspect their feet daily for any signs of wounds, blisters, redness, or other abnormalities. Early detection allows for prompt intervention and prevents minor issues from developing into serious complications.
- Wash and Dry Feet: Clean the feet daily with mild soap and lukewarm water, ensuring to dry them thoroughly, especially between the toes. Moisture can increase the risk of infections, so keeping the feet clean and dry is essential.
- Protect the Skin: Use a moisturizer to keep the skin on the feet soft and supple, but avoid applying it between the toes where moisture can accumulate. Additionally, use a barrier cream or petroleum jelly to protect vulnerable areas from friction and pressure.
- Trim Nails Carefully: Trim toenails straight across and avoid cutting into the corners to prevent ingrown toenails and potential wounds. If necessary, seek professional assistance from a podiatrist for nail care.
- Wear Proper Footwear: Diabetic individuals should wear properly fitting shoes with ample room for the toes and good support. Avoid high heels, tight shoes, and open-toed sandals, as they can increase the risk of foot injuries.
- Manage Blood Sugar Levels: Keeping blood sugar levels within target ranges is crucial for promoting wound healing and preventing complications. Follow a healthy diet, exercise regularly, and monitor blood sugar levels as advised by a healthcare provider.
- Seek Prompt Medical Attention: If a wound, blister, or sore develops on the foot, seek prompt medical attention from a healthcare professional specializing in diabetic foot care. Early intervention can prevent complications and promote healing.
Techniques for Wound Management
- Debridement: Remove dead or damaged tissue from the wound to promote healing. Debridement can be done using sharp instruments, enzymatic agents, or autolytic dressings.
- Dressing Selection: Choose appropriate wound dressings based on the type and severity of the wound. Options include foam dressings, hydrogels, hydrocolloids, and alginate dressings, among others.
- Offloading: Offload pressure from the wound site using specialized footwear, shoe inserts, or total contact casts to prevent further tissue damage and promote healing.
- Infection Control: Manage infections promptly with antibiotics or antimicrobial dressings as prescribed by a healthcare provider. Keep an eye out for any indications of infection, like temperature, redness, swelling, or drainage.
- Compression Therapy: Use compression therapy to improve circulation and reduce swelling in diabetic individuals with venous insufficiency or edema. However, caution is needed in individuals with arterial disease to avoid compromising blood flow.
- Advanced Therapies: Consider advanced wound care modalities such as negative pressure wound therapy (NPWT), hyperbaric oxygen therapy (HBOT), or bioengineered skin substitutes for complex or non-healing wounds.
Conclusion
Wound care for diabetic feet is essential for preventing complications, promoting healing, and preserving foot health and function in diabetic individuals. By following best practices for wound care, including daily foot inspections, proper hygiene, and timely medical intervention, diabetic individuals can reduce the risk of foot ulcers, infections, and amputations, and maintain an active and healthy lifestyle despite diabetes-related challenges. Collaborating with a multidisciplinary team of healthcare professionals, including podiatrists, wound care specialists, and diabetes educators, can further optimize outcomes and improve the quality of life for individuals living with diabetes.
For any further queries, Plz visit drankitinterventionalradiologist.com