Understanding The Biopsy Process: What You Need To Know
Biopsy is a medical procedure crucial for diagnosing various diseases, particularly cancer. It involves the removal of a small sample of tissue or cells from the body for examination under a microscope. Understanding the biopsy process is essential for patients and their families as it helps alleviate anxiety and ensures informed decision-making regarding their healthcare. This article delves into the biopsy process, covering its types, indications, procedures, risks, and benefits.
Types of Biopsy
Biopsies are classified based on the location of the sample and the method of extraction. Common types include:
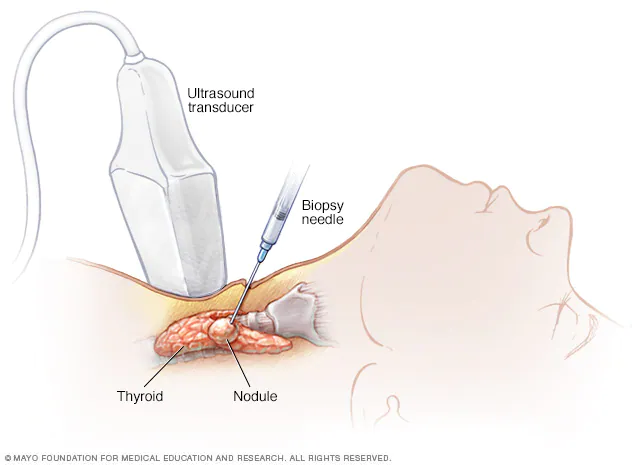
Needle Biopsy: Involves extracting tissue or fluid using a thin needle, often guided by imaging techniques like ultrasound, CT scans, or MRI.
Surgical Biopsy: Involves the removal of a tissue sample through a surgical incision.
Endoscopic Biopsy: Performed during endoscopy procedures to obtain samples from the digestive tract or respiratory system.
Bone Marrow Biopsy: Involves extracting bone marrow cells, typically from the hip bone, using a specialized needle.
Skin Biopsy: Obtains skin tissue for examination, often used to diagnose skin conditions or melanoma.
Indications for Biopsy
Biopsies are recommended when other diagnostic tests, such as imaging scans or blood tests, are inconclusive or suggestive of a particular condition. Common indications include:
- Suspicious lumps or masses detected during physical examination or imaging studies.
- Abnormalities are found during routine screenings, such as mammograms or colonoscopies.
- Symptoms suggestive of cancer, such as unexplained weight loss, persistent pain, or changes in bowel habits.
- Monitoring disease progression or treatment response, such as in cases of lymphoma or leukemia.
The Biopsy Procedure
The biopsy procedure may vary depending on the type and location of the sample being obtained. However, certain general steps are followed:
- Preparation: Patients may be instructed to refrain from eating or drinking for a specified period before the procedure. Depending on the type of biopsy, sedation or anesthesia may be administered to minimize discomfort.
- Sample Collection: The healthcare provider uses specialized instruments to obtain the tissue or fluid sample. This may involve inserting a needle through the skin or performing a surgical incision.
- Post-Procedure Care: After the biopsy, patients are typically monitored for any immediate complications, such as bleeding or infection. Depending on the site of the biopsy, they may be advised to avoid certain activities for a specified period.
Risks and Benefits
Like any medical procedure, biopsies carry risks and benefits that should be weighed carefully:
Risks: Potential risks of biopsy include bleeding, infection, pain or discomfort, and rare complications such as damage to nearby organs or tissues.
Benefits: Biopsy is a valuable diagnostic tool that can provide definitive information about the presence, type, and stage of a disease. Early diagnosis through biopsy allows for timely initiation of appropriate treatment, potentially improving outcomes.
Understanding Biopsy Results
Interpreting biopsy results requires specialized training and expertise. Pathologists analyze the tissue samples under a microscope, looking for abnormalities such as cancer cells, infection, inflammation, or structural changes. Patients should discuss the results with their healthcare provider, who can explain the findings in detail and recommend further steps, such as additional tests or treatment options.
Conclusion
In summary, understanding the biopsy process is essential for patients and their families facing diagnostic uncertainty or undergoing cancer screening. By familiarizing themselves with the types, indications, procedures, risks, and benefits of biopsy, individuals can approach the process with greater confidence and clarity. Effective communication with healthcare providers and active involvement in decision-making are crucial aspects of navigating the biopsy journey and achieving optimal health outcomes.
For any further queries, Plz visit drankitinterventionalradiologist.com