Current Research And Innovations In Uterine Artery Embolization
Uterine artery embolization (UAE) has emerged as a valuable minimally invasive treatment option for various gynecological conditions, particularly uterine fibroids. Over the years, ongoing research and technological innovations have contributed significantly to enhancing the efficacy, safety, and patient outcomes associated with UAE. This article explores the latest advancements in the UAE, highlighting current research endeavors and innovative techniques shaping the landscape of this procedure.
Understanding Uterine Artery Embolization
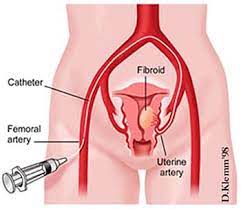
Uterine artery embolization involves the selective occlusion of blood vessels supplying the uterus, primarily to treat symptomatic fibroids. By cutting off the blood supply to these fibroids, UAE induces ischemia and subsequent shrinkage, alleviating symptoms such as heavy menstrual bleeding, pelvic pain, and pressure symptoms.
Targeted Embolization Techniques
Recent research has focused on refining embolization techniques to achieve more precise targeting of fibroids while minimizing damage to surrounding healthy tissue. Innovations such as microcatheters and advanced imaging modalities enable interventional radiologists to navigate the uterine vasculature with greater accuracy, leading to improved treatment outcomes and reduced complications.
Embolic Agents and Particle Size Optimization
The choice of embolic agents plays a crucial role in the success of the UAE. Ongoing research seeks to identify and optimize embolic agents that provide effective occlusion of uterine arteries while minimizing the risk of post-embolization syndrome and other adverse events. Additionally, there is a growing interest in tailoring particle size to achieve optimal embolization outcomes, with studies exploring the impact of different particle sizes on fibroid infarction and symptom resolution.
Patient-Centered Approaches
Advancements in UAE research are increasingly focused on personalized, patient-centered care. This includes identifying predictors of treatment response, refining patient selection criteria, and developing decision-making tools to guide clinicians and patients in choosing the most appropriate treatment option. By considering individual patient factors and preferences, researchers aim to optimize treatment outcomes and enhance patient satisfaction.
Combination Therapies and Adjunctive Treatments
Innovative approaches involve combining UAE with other modalities to enhance efficacy or address specific patient needs. For example, studies have investigated the use of pre-procedural hormonal therapy to optimize fibroid size and vascularity before embolization, potentially improving treatment outcomes. Additionally, adjunctive treatments such as drug-eluting microspheres or targeted drug delivery systems are being explored to enhance the therapeutic effects of UAE and minimize recurrence rates.
Fertility Preservation
Preserving fertility is a priority for many women seeking treatment for symptomatic fibroids. Recent research has focused on assessing the impact of the UAE on fertility outcomes and exploring strategies to optimize fertility preservation in women undergoing the procedure. This includes investigating the safety and feasibility of UAE in women desiring future pregnancy, as well as developing protocols for counseling and follow-up care to support reproductive goals post-embolization.
Quality of Life and Long-Term Outcomes
Beyond symptom relief, researchers are increasingly interested in evaluating the impact of the UAE on overall quality of life and long-term patient outcomes. Longitudinal studies are underway to assess the durability of symptom improvement, recurrence rates, and the need for re-intervention following UAE. Additionally, researchers are exploring patient-reported outcomes and satisfaction measures to understand better the holistic impact of UAE on women’s lives.
Cost-Effectiveness and Health Economics
As healthcare systems strive to optimize resource allocation and cost-effectiveness, there is growing interest in assessing the economic implications of UAE compared to other treatment modalities such as hysterectomy or myomectomy. Health economic studies are evaluating the direct and indirect costs associated with UAE, including procedural costs, hospitalization expenses, and long-term follow-up care. By incorporating cost-effectiveness data into clinical decision-making, researchers aim to inform healthcare policy and practice to maximize value for patients and healthcare systems alike.
Conclusion
Current research and innovations in uterine artery embolization hold great promise for advancing the field and improving patient outcomes. From targeted embolization techniques to personalized approaches and fertility preservation strategies, ongoing efforts are reshaping the landscape of the UAE and expanding treatment options for women with symptomatic fibroids. By translating research findings into clinical practice, healthcare providers can continue to offer safe, effective, and patient-centered care to women seeking relief from fibroid-related symptoms.