Breast Fibroadenoma: Emerging Trends In Diagnosis And Treatment
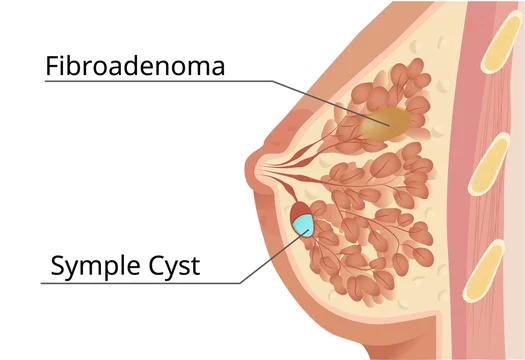
Breast fibroadenomas are common benign breast tumors that predominantly affect young women. While they are non-cancerous, fibroadenomas can cause discomfort and anxiety due to their palpable presence in the breast tissue. Over the years, significant advancements have been made in both the diagnosis and treatment of breast fibroadenomas, leading to more accurate detection and improved management strategies. In this article, we explore the emerging trends in the diagnosis and treatment of breast fibroadenoma, highlighting the latest innovations and promising developments in the field.
Enhanced Imaging Techniques
In recent years, there has been a shift towards utilizing advanced imaging modalities for the diagnosis of breast fibroadenomas. High-resolution ultrasound, in particular, has emerged as a valuable tool for characterizing breast lesions, including fibroadenomas. Real-time ultrasound elastography and shear wave elastography are innovative techniques that provide additional information about tissue stiffness, aiding in the differentiation between benign and malignant lesions. Additionally, contrast-enhanced ultrasound (CEUS) has shown promise in improving the detection and characterization of breast fibroadenomas, especially in cases where conventional ultrasound findings are inconclusive.
Molecular Imaging
Molecular imaging techniques, such as positron emission tomography (PET) and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), are being explored for their potential role in the diagnosis and characterization of breast fibroadenomas. PET imaging using radiotracers specific to cellular proliferation has shown promising results in distinguishing benign from malignant breast lesions. Similarly, dynamic contrast-enhanced MRI (DCE-MRI) provides functional information about tissue vascularity and perfusion, aiding in the differentiation of fibroadenomas from other breast lesions.
Minimally Invasive Biopsy Techniques
Traditional biopsy methods, such as core needle biopsy and fine-needle aspiration cytology, remain the gold standard for diagnosing breast fibroadenomas. However, emerging trends in minimally invasive biopsy techniques are revolutionizing the field. Vacuum-assisted biopsy (VAB) allows for the removal of larger tissue samples under imaging guidance, reducing the need for repeat biopsies and improving diagnostic accuracy. Additionally, image-guided percutaneous cryoablation is gaining traction as a minimally invasive treatment option for selected cases of symptomatic fibroadenomas, offering patients a scar-free alternative to surgical excision.
Personalized Medicine Approaches
Advances in molecular profiling and genomic analysis have paved the way for personalized medicine approaches in the management of breast fibroadenomas. Gene expression profiling studies have identified distinct molecular subtypes of fibroadenomas with varying clinical behaviors and prognoses. This molecular stratification may guide treatment decisions and help identify patients who are at higher risk of recurrence or progression. Furthermore, targeted therapies aimed at specific molecular pathways implicated in fibroadenoma development are being investigated as potential treatment options, offering the promise of more tailored and effective interventions.
Non-Surgical Management Strategies
In recent years, there has been growing interest in non-surgical management strategies for breast fibroadenomas, particularly among young women who wish to preserve their breast aesthetics and avoid surgery-related complications. Watchful waiting with regular clinical and imaging surveillance is often recommended for asymptomatic fibroadenomas, especially those with characteristic imaging features and reassuring clinical findings. Additionally, the use of oral contraceptives containing progestins or selective estrogen receptor modulators (SERMs) has shown promise in reducing the size and symptoms of fibroadenomas in some patients.
Patient-Centered Care
Emerging trends in the diagnosis and treatment of breast fibroadenomas place a strong emphasis on patient-centered care and shared decision-making. Healthcare providers are encouraged to engage patients in discussions about their treatment preferences, goals, and concerns, empowering them to actively participate in the decision-making process. Patient education and support programs play a crucial role in ensuring that individuals with breast fibroadenomas are well-informed about their condition and treatment options, enabling them to make informed choices that align with their values and preferences.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the diagnosis and treatment of breast fibroadenomas have witnessed significant advancements in recent years, driven by emerging trends in imaging technology, biopsy techniques, personalized medicine, and patient-centered care. These developments hold the promise of more accurate diagnosis, tailored treatment approaches, and improved outcomes for individuals affected by breast fibroadenomas. As research continues to progress and innovative technologies evolve, it is essential for healthcare providers to stay abreast of these emerging trends and incorporate them into clinical practice to optimize patient care and enhance the overall management of breast fibroadenomas.
For any further queries, Plz visit drankitinterventionalradiologist.com